Home > What is SCADA?

Revolutionize Plant Operations with SCADA and CMMS Integration
Integrating SCADA with MPulse CMMS gives maintenance teams real-time data for smarter, condition-based maintenance. This powerful combination streamlines asset management, reduces downtime, and enhances efficiency by triggering automated work orders only when needed. Maximize uptime and extend asset life with seamless SCADA system and MPulse integration.
Table of Contents
What is SCADA?
SCADA, which stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition, is an advanced system used to monitor, control, and collect data from industrial processes. By combining both software and hardware, SCADA enables real-time data analysis and remote management of industrial equipment, enhancing operational efficiency and system reliability across various industries. This powerful system not only ensures smooth operations but also provides valuable insights that support informed decision-making and optimization of industrial workflows. With SCADA, businesses can improve control, reduce downtime, and drive productivity in their operations.
How SCADA Works
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) software serves as a powerful bridge, connecting industrial equipment with operators and maintenance personnel. By facilitating the transmission of data from physical machinery to operator display screens, SCADA enables technicians to remotely monitor, control, and maintain assets across vast industrial environments.
Key tasks within a SCADA system include monitoring sensors and devices installed at remote substations, tracking system events for analysis, and adjusting process parameters like speed and operational levels from a central location. This centralized control empowers operators to make real-time adjustments without needing to physically interact with equipment.
Modern SCADA systems offer significant advantages by allowing technicians to oversee and manage a wide array of assets, locations, and systems from one central hub. The automation provided by SCADA systems boosts operational efficiency, enabling better decision-making, enhanced safety, and optimized resource management. Ultimately, SCADA helps improve productivity, reduce operational costs, and drive revenue growth.
Key Components of a SCADA System
A SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) system acts as a vital bridge between industrial equipment and operators, allowing seamless communication and efficient monitoring of operations. To transmit real-time data from machinery to operators, SCADA relies on several key components that work together to optimize performance and ensure operational efficiency.
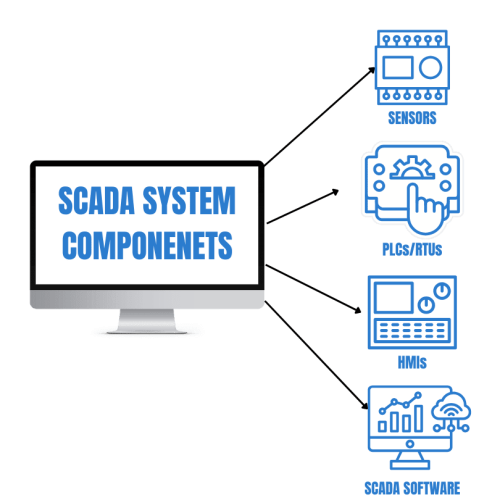
Sensors and Manual Input
SCADA sensors are essential for collecting data from various parts of an industrial plant. These sensors can range from simple binary sensors (e.g., on/off signals) to more complex ones that measure flow rates, temperature, and pressure. Operators and technicians can also manually input data into the SCADA system when needed, further enhancing system flexibility.
Conversion Units (RTUs & PLCs)
The data captured by sensors must be converted into actionable information for operators. This is where Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) and Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) come into play. These devices aggregate data from sensors and convert it into usable formats, ensuring that large volumes of system data are accurately processed and transmitted for analysis.
Human-Machine Interface (HMI)
The Human-Machine Interface (HMI) is a crucial element of SCADA systems. It displays processed data to operators, allowing them to easily understand and act on the information. The HMI provides a comprehensive overview of the entire process or system, enabling operators to visualize machine performance, control processes, and quickly respond to any faults or issues. Though it works hand-in-hand with SCADA, the HMI is specifically designed to present data in a user-friendly manner.
Communication Infrastructure Network
SCADA systems rely on a robust communication infrastructure network to connect all components across the plant. Traditionally, telephone lines and circuits were used for this purpose, but newer technologies such as wireless networks, radio waves, and cellular satellite communication are now widely used. This network ensures that real-time data flows seamlessly from the field to the central system, enabling remote monitoring and control of operations.
Together, these SCADA components create a unified system that allows for effective monitoring, control, and optimization of industrial processes. SCADA systems are instrumental in enhancing productivity, reducing downtime, and enabling more efficient maintenance and troubleshooting.
SCADA Systems Contribute to Maintenance and Reliability Efforts
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems are a vital asset in improving maintenance and reliability across industries. By providing real-time monitoring and control of complex industrial processes, SCADA systems ensure that technicians and operators can oversee operations both on the shop floor and at remote substations. This level of oversight is essential for optimizing maintenance and reliability efforts, enhancing productivity, and reducing downtime.
SCADA and Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM)
Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) is a strategy that prioritizes asset reliability and aims to optimize an organization’s entire maintenance system. RCM helps identify potential failure modes, allowing for proactive maintenance scheduling and minimizing unexpected breakdowns. SCADA systems complement RCM by providing real-time, automated data on asset performance, enabling early detection of issues before they result in system failures. This synergy ensures that maintenance teams can address problems promptly, reducing the likelihood of costly downtime or operational disruptions.
Real-Life Applications
Automating Electric Distribution
SCADA systems are crucial in managing electrical grids, where maintaining reliable power distribution is essential. In the electrical utility industry, SCADA sensors collect data from various substations, monitor system conditions, and send alerts for potential outages. Additionally, SCADA systems can automate repairs and pinpoint issues, significantly reducing response times and improving system reliability. With built-in redundancy checks, SCADA systems enhance the overall reliability of the power grid.Identifying Failures on a Production Floor
In manufacturing, early failure detection is critical to maintaining high levels of uptime. SCADA systems help identify issues before they escalate into major problems. For example, if a steam turbine component begins to fail, SCADA sensors can detect the malfunction and notify the maintenance team before the situation worsens. By addressing the issue early, companies can avoid catastrophic failures, prevent costly damage, and protect employee safety.Managing Sensitivity and Security in IT
SCADA systems also play a key role in IT and telecom sectors by monitoring sensitive environments, such as data centers. Sensors within a SCADA system track parameters like temperature and humidity, helping to prevent damage to IT equipment. Additionally, SCADA integrates with security systems to monitor alarms, door sensors, and motion detectors, enhancing both security and environmental control.Nerve Center of Alternative Energy
SCADA systems are essential for the growing field of renewable energy, particularly in wind farms. SCADA technology connects turbines, substations, and weather monitoring equipment, providing near real-time insights into performance and environmental conditions. This enables operators to monitor energy output, identify issues, and optimize turbine performance. SCADA systems also track energy generation data, helping with warranty claims and ensuring optimal operation in response to changing weather conditions.
SCADA Systems Contribute to Maintenance and Reliability Efforts
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems are a vital asset in improving maintenance and reliability across industries. By providing real-time monitoring and control of complex industrial processes, SCADA systems ensure that technicians and operators can oversee operations both on the shop floor and at remote substations. This level of oversight is essential for optimizing maintenance and reliability efforts, enhancing productivity, and reducing downtime.
SCADA and Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM)
Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) is a strategy that prioritizes asset reliability and aims to optimize an organization’s entire maintenance system. RCM helps identify potential failure modes, allowing for proactive maintenance scheduling and minimizing unexpected breakdowns. SCADA systems complement RCM by providing real-time, automated data on asset performance, enabling early detection of issues before they result in system failures. This synergy ensures that maintenance teams can address problems promptly, reducing the likelihood of costly downtime or operational disruptions.
SCADA in Real-Life Applications
Automating Electric Distribution
SCADA systems are crucial in managing electrical grids, where maintaining reliable power distribution is essential. In the electrical utility industry, SCADA sensors collect data from various substations, monitor system conditions, and send alerts for potential outages. Additionally, SCADA systems can automate repairs and pinpoint issues, significantly reducing response times and improving system reliability. With built-in redundancy checks, SCADA systems enhance the overall reliability of the power grid.Identifying Failures on a Production Floor
In manufacturing, early failure detection is critical to maintaining high levels of uptime. SCADA systems help identify issues before they escalate into major problems. For example, if a steam turbine component begins to fail, SCADA sensors can detect the malfunction and notify the maintenance team before the situation worsens. By addressing the issue early, companies can avoid catastrophic failures, prevent costly damage, and protect employee safety.Managing Sensitivity and Security in IT
SCADA systems also play a key role in IT and telecom sectors by monitoring sensitive environments, such as data centers. Sensors within a SCADA system track parameters like temperature and humidity, helping to prevent damage to IT equipment. Additionally, SCADA integrates with security systems to monitor alarms, door sensors, and motion detectors, enhancing both security and environmental control.Nerve Center of Alternative Energy
SCADA systems are essential for the growing field of renewable energy, particularly in wind farms. SCADA technology connects turbines, substations, and weather monitoring equipment, providing near real-time insights into performance and environmental conditions. This enables operators to monitor energy output, identify issues, and optimize turbine performance. SCADA systems also track energy generation data, helping with warranty claims and ensuring optimal operation in response to changing weather conditions.
The Evolution and Future of SCADA
SCADA systems have evolved significantly since their inception in the 1970s. Originally reliant on monolithic mainframe systems, SCADA has advanced to distributed systems, using PCs, local area networks, and ethernet for more efficient data sharing and integration. Today, SCADA systems are highly interconnected, leveraging SQL databases and linking seamlessly with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems for streamlined operations.
As industries continue to embrace emerging technologies, SCADA systems are becoming even more sophisticated. The integration of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), cloud computing, and advanced web technologies promises to enhance SCADA’s capabilities further, making it an essential tool for modern industrial operations. According to market research, the industrial control systems market, including SCADA, is expected to reach $181.6 billion in 2024, underscoring the growing importance of SCADA in maintaining operational efficiency, safety, and profitability.
How a CMMS Integrates with SCADA Systems
Maintenance and reliability teams can significantly enhance their operations by integrating a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) with SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems. This integration unlocks valuable real-time data, enabling teams to adopt condition-based maintenance strategies that improve asset management and system reliability.
The Challenge: Siloed Data and Lack of Access
In many industrial environments, production monitoring data is siloed, leaving operations teams with access to real-time asset data through SCADA systems, but maintenance teams without a comprehensive data acquisition tool. This gap can hinder the ability to make informed maintenance decisions and proactively manage asset health.
The Solution: MPulse CMMS and SCADA Integration
MPulse, a leading CMMS, addresses this issue by seamlessly integrating with SCADA systems, along with other industrial systems like Building Management Systems (BMS/BAS), Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES/MOM), and Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs). Once connected, MPulse captures SCADA measurements, allowing users to define the types of data to collect, the assets to monitor, and the frequency of data collection.
Enhancing Maintenance with Condition-Based Strategies
SCADA and CMMS integration empowers maintenance and reliability teams to implement condition-based maintenance (CBM). CBM focuses on performing maintenance based on the actual condition and usage of assets—such as temperature or run hours—rather than relying on scheduled intervals. This proactive approach ensures maintenance is conducted only when necessary, optimizing asset performance and extending lifespan.
The Pitfalls of Other Maintenance Strategies:
- Reactive Maintenance: Performed in response to unexpected failures, reactive maintenance often comes too late to prevent significant damage or downtime.
- Preventive Maintenance: Based on arbitrary time schedules, preventive maintenance can lead to either under-maintenance (causing failures) or over-maintenance (wasting resources, time, and labor).
With condition-based maintenance powered by SCADA and CMMS integration, maintenance is performed at the optimal time, based on real-time asset data. For example, when a motor exceeds its normal operating temperature, the SCADA system triggers an alarm. This alarm then sends a signal to MPulse, which automatically generates a work order, ensuring timely maintenance to prevent potential issues.
Real-Time Alerts and Automated Work Orders
MPulse’s integration with SCADA systems allows maintenance teams to set up automated condition-based work orders triggered by specific alarms or data thresholds. If an asset’s performance falls outside of set parameters, such as abnormal temperature readings or excessive vibration, MPulse generates a work order automatically, ensuring the necessary action is taken before a failure occurs.
The Benefits of SCADA-CMMS Integration
By connecting your CMMS to your SCADA system, maintenance and reliability teams gain access to invaluable real-time data that enhances decision-making and resource allocation. This integration helps to maximize uptime, improve asset reliability, and optimize production processes, ultimately driving greater operational efficiency and profitability.
Incorporating SCADA into your CMMS workflow allows your organization to implement condition-based maintenance strategies that are more precise, effective, and resource-efficient than traditional preventive or reactive approaches. With the right tools, like MPulse, your team can stay ahead of potential issues and maintain peak performance across your industrial assets.
MPulse Means Happy Customers